
This problem appears not to be iperf3-specific, and may be due to the placement of the iperf3 process on a CPU and its relation to the inbound NIC. The symptom is that on any particular run of iperf3 the receiver reports a loss rate of about 20%, regardless of the ``-b`` option used on the client side. UDP performance: Some problems have been noticed with iperf3 on the ESnet 100G testbed at high UDP rates (above 10Gbps).These issues are either open (indicating no solution currently exists) or closed with the notation that no further attempts to solve the problem are currently being made: The following problems are notable known issues, which are probably of interest to a large fraction of users or have high impact for some users, and for which issues have already been filed in the issue tracker. Then submit to the iPerf3 issue tracker on GitHub: Known Issues To see the collection of prior postings to the list, visit the Iperf-users Archives.īefore submitting a bug report, try checking out the latest version of the code, and confirm that it’s not already fixed. To post a message to all the list members, you need to subscribe to Iperf-users. Your public IPv6 address is : You do not have IPv6 connectivity (Reverse DNS: n/a).New: Disk write tests (server: iperf3 -s -F filename / client: iperf3 -c testhost -i1).New: Disk read test (server: iperf3 -s / client: iperf3 -c testhost -i1 -F filename).New: Output in JSON format (-J option).New: Use SCTP rather than TCP (-sctp option).New: Set congestion control algorithm (-C option).New: Set target bandwidth for UDP and (new) TCP (-b option).

Client and server can have multiple simultaneous connections (-P option).Cross-platform: Windows, Linux, Android, MacOS X, FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD, VxWorks, Solaris.Client can create UDP streams of specified bandwidth.Support for TCP window size via socket buffers.Report MSS/MTU size and observed read sizes.It is released under a three-clause BSD license. iPerf was orginally developed by NLANR/DAST.
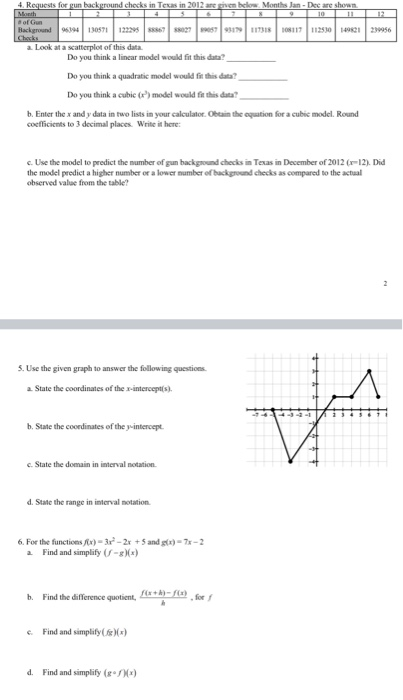
3.1.3 TESTOUT LAB CODE
This is a new implementation that shares no code with the original iPerf andĪlso is not backwards compatible. It supports tuning of various parameters related to timing, buffers and protocols (TCP, UDP, SCTP with IPv4 and IPv6).įor each test it reports the bandwidth, loss, and other parameters.
3.1.3 TESTOUT LAB MAC
Your company purchase a new bridge, which filters packets based on the MAC address of the destination computer.IPerf3 is a tool for active measurements of the maximum achievable bandwidth on IP networks. Match the network function or device on the left with the OSI model layer it is associated with on the right.Īpplication-HTTP Presentation-ASCII Session-Session ID Number Transport-Port Numbers Network-Router Data Link-Switch Physical-Wireless Access PointĪt what OSI layer does a router operate to forward network messages?

Presentation-Application Data Link-Network Interface Application-Application Session-Application Network-Internet Transport-Transport Each option on the left can be used more then one. Match each layer of the TCP/IP model on the left with the corresponding layer of the OSI model on the right. Which OSI Model layer is responsible for guaranteeing reliable message delivery? Defining a unique hardware address for each device on the network -Letting devices on the network have access to the LAN Which of the following are functions of the MAC sublayer? (Select two)

The Data Link Later of the OSI Model is comprised of two sublayers. Which of the following functions are performed at the Physical Layer of the OSI Model? Integration of network functionality into the host operating system -Enabling communication between network clients and services In the OSI Model, which of the following functions are performed at the Application Layer? Specify data format -Encrypt and compress data In the OSI Model, which of the following functions are performed at the Presentation Layer? In the OSI Model, what is the primary function of the Network Layer? Identifying physical network device -Controlling how messages are propagated through the network Which two of the following are included as part of the Data Link Layer?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
